Sustainable Environment Design 
Park 101 will be located in the City of Los Angeles. It is a project of the City of Los Angeles with the support of the Southern California Association of Governments (SCAG). The main reason for capping the park is to reconnect the city’s historic core, north of the freeway with the cultural, civic, and financial cores of the modern Los Angeles to the south. More so, it is aimed at catalyzing urban renewal and improving sustainability in the City of Los Angeles. Park 101 could be categorized as a deck type of park because it will come in the form of a sunken highway that will improve the face of the whole city and ensure the modern generation is able to enjoy. The funding of the project comes from the Southern California Association of Governments and the estimated cost is believed to be around $ 825 million over the next 25 or more years.
The Central Artery/Tunnel Project is also commonly referred to as the Big Dig. It is located in Boston. The project was mainly capped to help eliminate the challenge of pedestrians closing and improving the environmental outlook of the city by providing a green cover. The planning phase of the project began in 1982 and the construction was officially started in 1991 and officially completed on December 31, December 2007. The Big Dig could be categorized as a cut and cover tunnel, and it connects the neighborhoods in the most effective manner possible. The federal government funded the project after the approval of the Congress in 1987. It is important to note that the project cost an estimated $14 billion hence standing out as the most expensive public highway project in the history of the United States of America.
Categories/Types of Projects
There are four common types of projects that could be identified. The freeway capping process is also usually referred to as a deck, cut and cover tunnel, platform, and bridge widening. These form the common types of projects. The deck entails the use of a sunken highway to create connections between the different areas of a particular area. The perfect example of a project that falls in the deck category is Park 101, which has been proposed in the City of Los Angeles. Another category is the platform that is normally used for the normal grade highway. The best example of a platform is the Freeway Park in Seattle. The third category of these projects is the cut and cover tunnel. The cut and cover tunnel is usually used for elevated highways. The Big Dig project in Boston is a key example of the cut and tunnel. The fourth category is bridge widening. Bridge widening works in line with the “maximum green” concept where the environment is always prioritized. The key example in this category is the Brooklyn-Queens Expressway (BQE) enhancement project by NYCEDC.
Real Challenges in Capping Freeways
The key challenge in capping freeways is the high construction costs. It is worth noting that the construction costs for cap parks are extremely high especially for the large ones. The cost for constructing the largest cap projects are extremely high and the financing bodies always have to ensure that they do their best to meet these costs. For example, the cost of the Big Dig project was extremely high because of the yearly escalations in the course of its construction. However, in the eyes of the public, these costs are not that high, especially because of the misunderstanding of the cap projects. The Big Dig project cost an estimated $14 billion that had not been anticipated when the project was initially started in 1991. Accordingly, officials has originally predicted a 2005 completion date for the park components of the Greenway. Nevertheless, there were numerous delays, the collapse of the Big Dig, a cost-overruns that ensured the project ended in 2007. The $14 billion price tag that was suggested in 2007 surprised many people and raised questions on the financial feasibility of such projects in the country. It is important to note that this was mainly made up of a transportation project and included under water tunnels and major bridges. At least $40 million (of the $14 billion) was spent on the mile stretch of the four parks that make up the Greenway. The high cost makes it difficult to complete these projects at the required time. The chart below illustrates the view that that cap projects are costly.
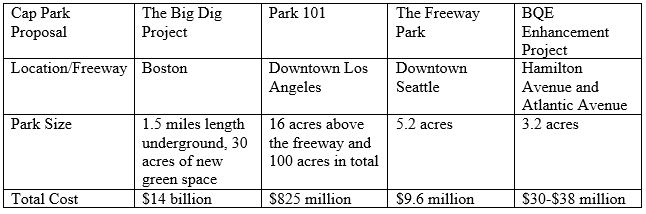
The Sources of Funding for Freeway Capping Projects
The freeway capping projects derive their financing from various sources that lead to their completion. The existence of numerous sources of financing ensures that all these projects are completed in the easiest manner possible with the existing financial resources. Here is an explanation of the sources of funding for the four capping cases utilized in this research.
- The main source of funding for the Big Dig project was the federal government. It is necessary to note that the Congress approved the money for the construction of the Big Dig project hence ensuring there were adequate financial resources to deal with it to the end. The federal government offered the required funds that played an important role in the construction process. However, there were cases when the federal government seemed to delay the project.
- The key source of funding for Park 101 will be the Southern California Association of Governments (SCAG). The SCAG has prepared itself to meet the financial requirements of the project over the next 15 years or more. The cooperation among these governments will be helpful in leading to the completion of the project in the coming days.
- The Freeway Park in Seattle got its funding from the ‘ Forward Thrust’ bond issues that happened in the 1960s. Jim Ellis was on the frontline in terms of ensuring that adequate financing is raised to finance the project and ensure its sustainability into the future.
- The BQE enhancement project derived its funding from stakeholders and the existing political will and support. The community was able to work together with the local government to ensure that the project is boosted in the course of its development to improve both pedestrian and motor ways.
Considerations at the Beginning and During the Construction
The Big Dig project provides effective opportunities for coming up with important considerations at the beginning and during the construction process to avoid excessive costs and delays in the completion of the project.
- The first factor to consider is the sufficiency of the funds required for the completion of the required project. Make sure that the funds available for the completion of the project are sufficient in line with the amount of work involved and the time it would take to complete the project. Again, Big Dig represents some of the projects that give poor examples where this factor was not considered. There were many instances of guessing hence leading to the incurrence of excessive costs.
- The second factor that should be considered is the planning of the traffic during construction to avoid interruptions on the flow of traffic. Well-planning of the traffic flow will be helpful in ensuring that the normal system of operation is not interfered with. It will also avoid any form of damages to the project under construction hence leading to its long-term survival and completion.
- In my opinion, advances in engineering technologies should also be considered at the beginning and during the construction process. The consideration of engineering technologies is helpful because it presents the best opportunities for financiers of the project to select the most reliable and effective techniques that will lead to the successful completion of the project.
Reducing the Cost
- One of the best ways of reducing the associated costs is to ensure that the land space above the freeway is free and made available as air rights by Caltrans. This will be an important multimillion dollar gift to urban locations looking forward to put up capping parks. For instance, the normal cost of land is approximately $2 to $3 million per acre near the Santa Ana Freeway by the Los Angeles City Hall. The provision of land for free will ensure that costs are reduced because their will be no need to incur land costs. Nevertheless, this might not be likely because the Caltrans could identify themselves as the key stakeholders in the constriction of Park 101. This also serves as an advantage to the success of the overall project. More so, Boston did sale this rights to allow for the construction of the Big Dig. This explains why it is one of the best and most expensive highways in the U.S. history at the moment.
- Another important way of helping to reduce costs of these projects is through the creation of a tax increment financing district where the future increased costs will be used to pay back the cost of the park. This could be achieved through economic analysis that gives a rational view on this economic balance. For example, the Park 101 proposal is expected to offer adjacent value creation opportunities that will come in the form of real estate development. There will be an estimated $1.25 in new private developments for every dollar of public investment.
Other Examples of Freeway Capping
The world is obviously excited when the concept of freeway capping is mentioned. The excitement comes from the potential benefits that are usually associated with such projects. Some of the key benefits that interest the world include the improvement of the environment and the improvement in the transportation channels. The excitement is always shared by different countries around the globe. However, the difference in the implementation of the concept arises from the availability of financial resources required to complete freeway capping projects.
Another example of freeway capping is the Trans-Canada Highway, which is believed to be the world’s longest national highway. It is a deck type of highway and has made everything in the country more efficient.
This strategy has not been brought out because of the complexities associated with it. It is still complex to understand and implement quickly because countries have to keep following the stated procedures in the best manner possible. We will only be able to bring it out when these complexities are reduced to the easiest approach in the completion of projections.
Conclusion
I think this movement is still at infancy because it is still a trend that is only trying to gain popularity. It cannot gain popularity over time because it needs time to be understood effectively. The sunken highways in big cities are still not popular in many parts of the world hence indicating that the idea is still at infancy. The deck type differs from the cut and cover, and platform type of highway because it does not require the removal of the highway itself.


